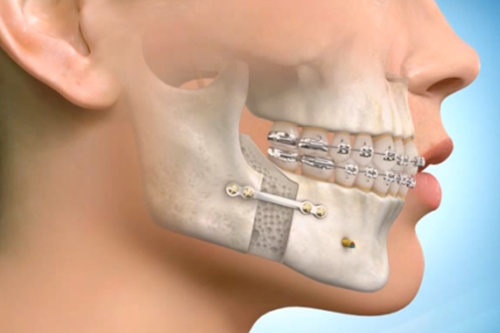
Jaw surgery, medically known as orthognathic surgery, is a specialized procedure aimed at correcting irregularities of the jaw bones and realigning the jaws and teeth to improve function, appearance, and overall oral health. This surgery is often considered when traditional orthodontic treatments هزینه عمل فک و چانه, like braces, alone cannot fix problems related to jaw alignment or bite.
Why Jaw Surgery May Be Needed
Jaw surgery is typically recommended for people who have significant jaw misalignment that causes:
-
Difficulty chewing or biting
-
Speech problems
-
Chronic jaw or TMJ (temporomandibular joint) pain
-
Sleep apnea or breathing issues due to jaw positioning
-
Facial asymmetry or aesthetic concerns
-
Open bite, overbite, or underbite that cannot be corrected with orthodontics alone
Common conditions treated with jaw surgery include:
-
Malocclusion (bad bite)
-
Jaw deformities caused by injury, birth defects, or developmental issues
-
Facial trauma requiring reconstruction
-
Obstructive sleep apnea related to jaw position
Types of Jaw Surgery
Jaw surgery can involve one or both jaws depending on the specific condition:
-
Maxillary Osteotomy (Upper Jaw Surgery): Realigns the upper jaw to improve bite and facial profile.
-
Mandibular Osteotomy (Lower Jaw Surgery): Moves the lower jaw forward or backward for better occlusion and function.
-
Genioplasty (Chin Surgery): Often combined with jaw surgery to improve chin position and facial harmony.
The surgery is usually performed by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon in collaboration with an orthodontist who prepares the teeth before surgery and fine-tunes the bite afterward.
The Procedure
Before surgery, patients typically undergo months of orthodontic treatment to position teeth properly. The surgery itself is done under general anesthesia and involves making cuts in the jawbone to move it into the correct position. Plates, screws, or wires are used to stabilize the jaw during healing.
Recovery involves swelling, bruising, and dietary changes (often soft or liquid foods) for several weeks. Most patients return to normal activities within a few weeks but should avoid strenuous physical activity during the healing phase.
Benefits of Jaw Surgery
-
Improved bite function and chewing
-
Better speech clarity
-
Enhanced facial aesthetics and symmetry
-
Relief from jaw pain and TMJ disorders
-
Improved breathing and reduction in sleep apnea symptoms
Risks and Considerations
As with any surgery, jaw surgery carries risks including infection, nerve damage leading to temporary or permanent numbness, bleeding, and issues with jaw movement. Close monitoring by the surgical team and orthodontist helps minimize complications.
Is Jaw Surgery Right for You?
If you experience functional problems with your bite, facial asymmetry, or breathing issues, consult with an orthodontist or oral surgeon. They will evaluate your condition using clinical exams, X-rays, and possibly 3D imaging to determine if jaw surgery is the best course of action.